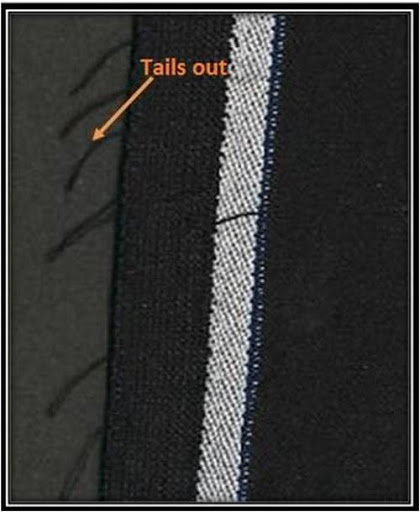
Sample sequence for Woven fabric
1.
Proto Sample /
Development Sample
2.
CS (Commercial Sample) / Ad. Sample/Sales
Sample
3.
APS (Fit) Sample èWill send to buyer ends.
4.
Size set sample
5.
APS finish sample (All actual) è Will send to buyer ends.
6.
FTL (Finish Tolerance Limit Sample) è Will send to buyer ends.
7.
ASOPCR sample è Will send to buyer ends.
8.
Lab test sample è Will send to buyer ends.
9.
FOP sample è Will send to buyer ends.
আজ এ পর্যন্তই । তবে এ যাওয়াই শেষ যাওয়া নয়। সামনে ইনশা’আল্লাহ দেখা হবে
নতুন কোন পর্ব নিয়ে আপনাদের মাঝে। তার আগ পর্যন্ত ভালো থাকুন, নিজে জানার জন্য,
নিজের অভিজ্ঞতা থেকে অন্যকে জানানোর জন্য Merchandising School এর সাথেই থাকুন।
আল্লাহ হাফেজ।
গার্মেন্টস স্যাম্পল এবং তার প্রকারভেদ
মার্চেন্ডাইজিং এ যেই শব্দটা সবচেয়ে বেশিবার
শুনবেন তা হচ্ছে Sample। কারণে অকারণে ইচ্ছায় অনিচ্ছায় আপনার চারপাশে এই শব্দটাই
সারাক্ষণ ঘুরবে আর তার সাথে সাথে আপনাকে ব্যতিব্যস্ত রাখবে। আর ট্রেইনিদের
ক্ষেত্রে সর্বপ্রথম যেই Responsibility বর্তায় তা হচ্ছে Sample Follow Up. আসুন
জেনে নেওয়া যাক Sample কি আর Sample কত প্রকার হতে পারে।
খাটিঁ বাংলা ভাষায় স্যাম্পল মানে হচ্ছে নমুনা।
অর্থাৎ বড় কোন অংশের Miniature Version অথবা কোন অংশবিশেষ হচ্ছে স্যাম্পল। স্যাম্পলের
পুথিগত কোন সংজ্ঞা আমার জানা নেই। আমার মতে কোন একটা গার্মেন্টের সরাসরি বৃহৎ
উৎপাদনে (Bulk Production) যাওয়ার আগে বিভিন্ন বায়ারের বিভিন্ন চাহিদা অনুযায়ী
নির্দিষ্ট উদ্দেশ্যে যে সকল নমুনা গার্মেন্ট বায়ারের অনুমোদনের (Approval এর) জন্য
বানানো এবং পাঠানো হয় তাকে স্যাম্পল বলে। বায়ার এমনি এমনি আপনাকে কোন একটা অর্ডার
Confirm করবে না। Order Confirm হওয়ার আগে এবং পরে নির্দিষ্ট কয়েক প্রকার
স্যাম্পল বায়ার কর্তৃক Approve হলেই আপনি Bulk Production করতে পারবেন এবং
গার্মেন্টস Shipment করতে পারবেন। আগেই বলেছি বিভিন্ন বায়ারের Requirements
অনুযায়ী স্যাম্পল অনেক প্রকার হতে পারে। তার মাঝ থেকে আসুন কিছু Common Sample
সম্পর্কে জেনে নেই -
১) Proto/Development
Sample :
যে কোন নতুন Style এর Development আসলে বায়ার ঐ
Style এর Sketch, measurements sheet & Trim sheet /BOM(Bills of Material) দেয়। সে অনুযায়ী প্রথম যেই স্যাম্পল পাঠানো হয়
তাকে Proto/Development Sample বলে। এই স্যাম্পলের প্রধান উদ্দেশ্য হচ্ছে Garments
এর Styling এবং তার পাশাপাশি যেই Vendor কে এই Development দেওয়া হলো তাদের
Workmanship অর্থাৎ তারা আসলে কতটুকু ভালোভাবে গার্মেন্ট Sewing এবং Wash করতে
পারে তা দেখা হয়। এই স্যাম্পলের উপর ভিত্তি করে বায়ার Comment করে এবং সেই অনুযায়ী
পরবর্তীতে আবার স্যাম্পল পাঠাতে হয়।
২) Wash Down Sample:
এই স্যাম্পলের প্রধান উদ্দেশ্য হচ্ছে গার্মেন্টের
ওয়াশ দেখা। বিশেহ করে ডেনিমের ক্ষেত্রে বায়ার একই রকম ফ্যাব্রিকের উপর বিভিন্ন রকম
ওয়াশ দেখতে চায়। সেজন্যই এই স্যাম্পল বানানো হয়।
৩) Fit Sample:
নাম শুনেই অনেকটা বুঝা যাচ্ছে এই স্যাম্পলের কাজ
কি হতে পারে । এই স্যাম্পলের কাজ হচ্ছে গার্মেন্টের Fit Approval নেওয়া অর্থাৎ
গার্মেন্টটা ঠিকমতো ফিটিং অনুযায়ী বানানো হচ্ছে কিনা তা চেক করা। একটা স্টাইলে
অনেকগুলো সাইজ থাকে। সব সাইজের জন্য ফিট স্যাম্পল বানাতে হয় না। এক্ষত্রে
নির্দিষ্ট একটি কিংবা দুইটি সাইজের স্যাম্পল বানিয়ে বায়ারে কাছ থেকে এপ্রোভাল
নেওয়া লাগে।আর ফিট স্যাম্পল এপ্রোভড হয়ে গেলে সে অনুযায়ী গ্রেডিং করে বাকি
স্যাম্পলগুলোর ফিটিং ঠিক করা হয়।
৪) Advertising Sample:
সাধারনত একটা স্টাইল মার্কেটে আসার দুই-আড়াইমা আগে
থেকেই বায়ার তাদের ওয়েবসাইটে এবং অনলাইন শপগুলোতে সে স্টাইলের promotion করে।
এগুলো সাধারনত মডেলরা পরে Photo shoot করে।
৫) SMS Sample (Sales
Man Sample):
এই স্যাম্পলগুলোও Promotional Purpose এ করা হয়।
তবে SMS Sample এর ক্ষত্রে যা করা
হয় তা হচ্ছে অর্ডার কনফার্ম করার আগে
বিভিন্ন স্টাইলের স্যাম্পল বায়ার তাদের স্টোরগুলোতে প্রেজেন্ট করে কাস্টমারদের
Feedback যাচাই করে এবং সে অনুযায়ী ভালো Feedback পাওয়া স্টাইলগুলোর অর্ডার
কনফার্ম করে।
৬) PP(Pre-Production)
Sample:
কোন একটা স্টাইলের প্রডাকশন শুরু হওয়ার আগে ফিট
এপ্রোভড পাওয়া মেজারমেন্ট দিয়ে এপ্রোভাল পাওয়া এবং বুকিং দিয়ে আনানো ফেব্রিক এবং
ট্রিমস দিয়ে স্যাম্পল Make করে Approve Wash Down স্যাম্পল অনুযায়ী ওয়াশ করে যে
স্যাম্পল এপ্রোভালের জন্য বানানো হয় তাকে PP Sample বলে । এই স্যাম্পল বানানোর
উদ্দেশ্য হচ্ছে এটা নিশ্চিত হওয়া যে Bulk production এ সবকিছু বায়ারের Requirement
অনুযায়ী হবে।
৭)Size Set Sample:
এই স্যাম্পল সাধারনত PP Sample Approved হওয়ার পর
এবং Bulk Cutting শুরু করার আগে বানানো হয়। যেহেতু শুধু নির্দিষ্ট দুই একটা সাইজের
উপর PP Sample করা হয় তাই সব সাইজের মেজারমেন্ট ঠিক আছে কিনা তা চেক করার জন্য সব
সাইজের স্যাম্পল বানিয়ে মেজারমেন্ট এবং প্যাটার্ন Adjustment Check করা হয়।
৮) TOP (Top of The
Production) Sample:
প্রডাকশন শুর করার পর সবকিছু ঠিকঠাক আছে কিনা তা
চেক করার জন্য বায়ার যেই স্যাম্পল চায় তাকে TOP Sample বলে। এটা সাধারণত Production শুরু হউয়ার কয়েক দিনের মাঝেই বায়ারের কাছে পাঠানো হয়।
৯) GPT (Garment
Package Test) Sample:
যে কোন বায়ারেরই Order Shipment করার আগে
International Third Party Testing Lab এ Bulk Production থেকে কিছু স্যাম্পল এনে
আগে টেস্ট করে চেক করে নেওয়া হয় যে, যেই Garment Shipment করা হবে তা আসলে
Physical Strength, Chemical Behavior, Safety এবং যেই দেশে shipment করা হবে
সেদেশের ল এবং সেই বায়ারের বিভিন্ন প্যারামিটার অনুযায়ী ঠিক আছে কিনা। একে GPT
Sample বলে।
এছাড়াও আরো বিভিন্ন বায়ারের Requirement অনুযায়ী
বিভিন্ন নামে বিভিন্ন প্রকার স্যাম্পল আছে।